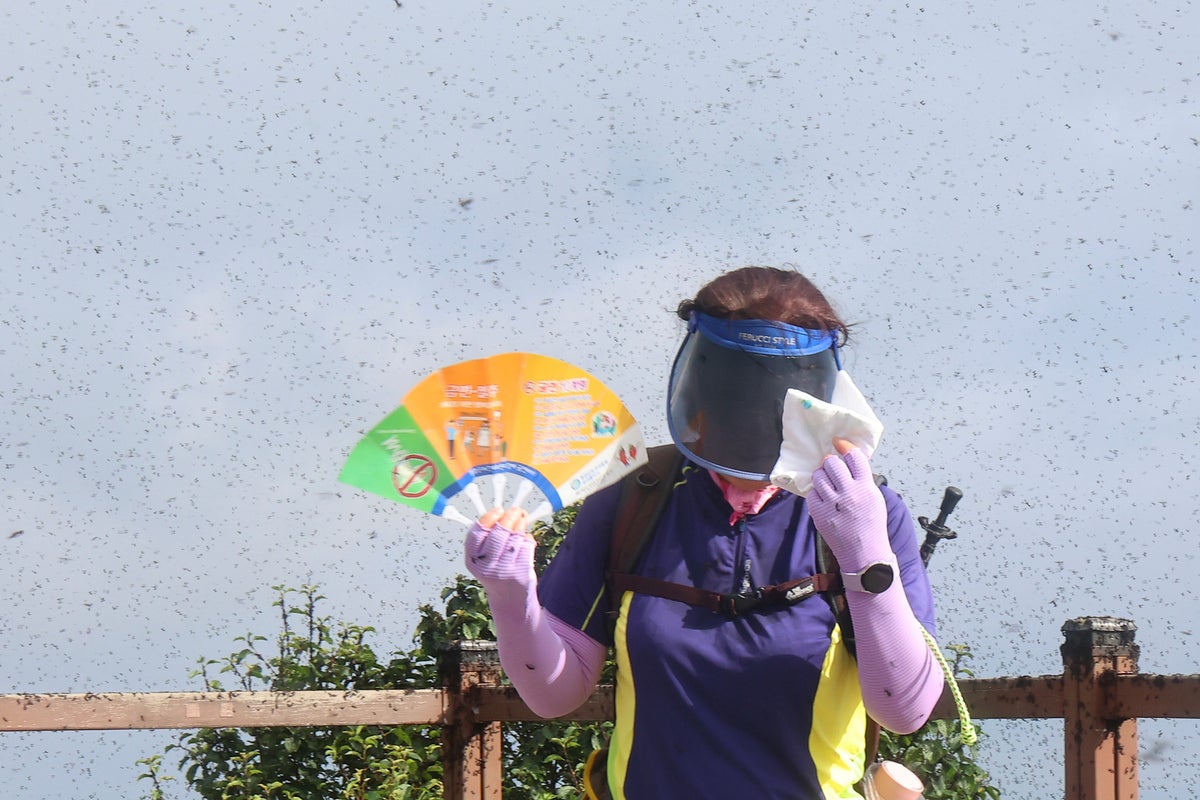
Residents in and round Seoul are battling clouds of bugs dubbed “lovebugs” which have blanketed climbing trails, remark decks, and common mountain paths.
Movies taken this week in Gyeyangsan Mountain, west of the capital, present bushes, railings, and stairs crawling with the small black-winged bugs, that are formally often known as Plecia longiforceps.
The bugs have earned the nickname “lovebugs” as a result of mating pairs fly whereas connected to one another. Whereas they don’t chunk or transmit ailments, their sheer numbers have turned out of doors areas into swarming black clouds, sparking alarm amongst hikers and vacationers.
Seoul’s metropolis authorities mentioned complaints have greater than doubled in a 12 months, hovering from round 4,400 in 2023 to over 9,200 final 12 months, as summer season temperatures rise and permit the subtropical species to thrive additional north.
Initially native to hotter climates, Plecia longiforceps has expanded its vary as South Korea warms, a pattern specialists hyperlink to local weather change. They had been first recognized in South Korea throughout a significant 2022 outbreak.
The bugs’ sudden proliferation has compelled officers to dispatch crews to common websites with water sprays and sticky traps, however Seoul’s authorities has discouraged folks from utilizing pesticides as a result of potential hurt to different bugs and the atmosphere.
“They’ve a disgusting look however are literally helpful bugs,” Seoul authorities mentioned in public bulletins.

Residents have been suggested to keep away from carrying vibrant colors and restrict time close to lights at night time, which magnetize the bugs in giant numbers.
Consultants say grownup lovebugs solely dwell just a few days, so the invasion ought to ease by mid-July, however officers warn the outbreaks may develop into an annual nuisance if temperatures proceed to climb.
Native tv stations confirmed scenes of remark decks swarming with the bugs, with staff continuously shovelling lifeless bugs from the bottom.
Wang Hyeon-jeong, an official from the Gyeyang district, confirmed the dramatic enhance, mentioned: “In contrast with the previous two years, the variety of lovebugs sharply surged final weekend on the mountain.”
The 395m (1,295ft) mountain gives the kind of sizzling, humid climate circumstances through which lovebugs sometimes thrive, the Surroundings Ministry mentioned, probably resulting in the insect inhabitants surge.

Lately, South Korea has skilled a sequence of unusually sizzling summers, with rising common temperatures extending additional into spring and autumn. Consultants imagine these hotter, longer summers are permitting subtropical species like lovebugs to maneuver north and survive in locations like Seoul and Incheon, which had been beforehand too cool for big populations to determine.
One other issue is city warmth islands: giant cities like Seoul could be a number of levels hotter than surrounding rural areas as a result of concrete and asphalt soak up and launch warmth, creating microclimates the place bugs tailored to hotter circumstances can thrive. Moisture from latest rains or monsoon intervals can additional speed up lovebug replica by offering perfect breeding circumstances.
Not simply lovebugs, however many bugs and different species are shifting into areas that had been as soon as too chilly for them as world temperatures rise because of the burning of oil, gasoline and coal.
In Europe, the tiger mosquito, a provider of dengue and chikungunya, has unfold north into France and Germany. Within the US, southern pine beetles have moved into forests of the northeastern states, damaging bushes that had been beforehand protected by colder winters.
Consultants say this poleward and uphill unfold of species is likely one of the most fast and visual impacts of the local weather disaster on ecosystems worldwide.